Listen to this article
For a company to establish itself and stand the test of time, it must take corporate risk management into account. This refers to the uncertainty of what will happen in the future after a business decision is made. Therefore, we can define risk management as the combination of strategies that enable a company to identify, prevent, and respond to events and actions that could threaten its usual operations, whether they are commercial, productive, or internal. In short: avoiding mistakes and decisions that lead down the wrong path.
Types of risks
In the day-to-day functioning of a company, it faces a wide variety of risks, which can vary depending on factors such as the sector it belongs to, its size, or its location. Some of the most common types of risks include:
• Fortuitous Risks: These are risks that cannot be controlled and usually take any company by surprise. The first example that comes to mind for most of us is health risks, like the recent COVID pandemic. This category also includes natural disasters such as earthquakes, fires, or floods. While we can’t predict when they will occur, we can prepare to face them and have a risk management plan ready for such eventualities.
• Financial Risks: These refer to market fluctuations, such as changes in interest rates, liquidity issues, and the prices of raw materials.
• Legal Risks: This isn’t just about dealing with potential lawsuits, warranty claims, or other types of complaints. Companies are subject to laws and certifications that regulate their operations and the distribution and sale of their products or services. Failure to comply with these can lead to penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
• Operational Risks: This category covers all dangers related to the company’s operations: from poorly executed strategies, human errors, or supply chain interruptions to risks associated with health and safety in the workplace, for example. These risks originate within the company’s internal activities but have negative effects on financial, productive, and commercial levels.
• Environmental and Social Risks: These include all risks related to the impact a company has on the environment, society, and local communities. Examples include risks associated with pollution, climate change, conflicts with stakeholders, and changes in government.
• Technological Risks: The improper use of technology and the lack of cybersecurity measures to protect businesses and their digital data are risks that should be considered in any corporate strategy.
Technology in Risk Management
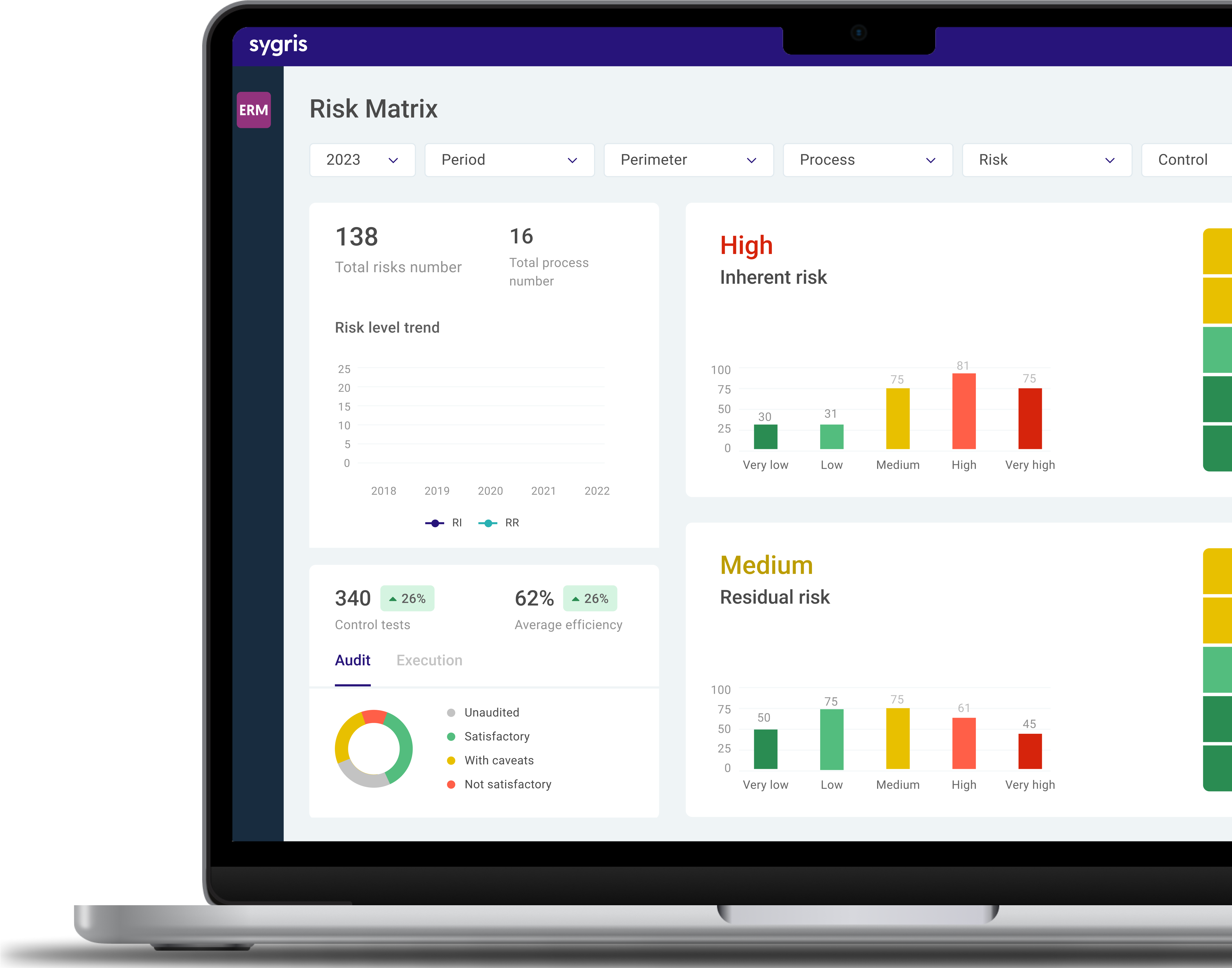
The key to managing the risks a company faces, minimising the likelihood of them occurring and, if they can’t be avoided, reducing their impact, lies in having a solid strategy and realistic, effective action plans. How? By implementing risk management software.
Risk management software leaves no room for improvisation, allowing companies to identify, manage, and assess the full spectrum of risks they face and activate the necessary mechanisms to mitigate them. Thanks to technology, businesses can analyse large volumes of data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that help them anticipate and prepare for potential risks. In this way, technology protects business operations, helps save costs, boosts productivity, and improves customer and employee satisfaction, among other benefits.
Sygris ERM technology enables the implementation of a system capable of managing any risk associated with business processes, ensuring the automation of processes and control testing, and establishing a three-line defence system. Shall we talk?